We created the Home Furniture app to explore the effects of deceptive patterns on user decision-making. Through A/B testing, we hope to gain valuable insights into how design patterns influence user behaviour. Our goal is to promote ethical design, and transparency, and enhance user experiences based on our findings.
Responsibilities
- Ethical Design
- User Research
- Usability Testing
- Design Iterations
- Data Analysis
Deliverables
- Case Study Report
- Wireframes
- High-Fidelity Figma Designs
- Usability Test Results
- Design Recommendations
My role
UX Designer/Researcher
Duration
July 2023 to September 2023
The challenge
Our challenge was twofold: to design an app where two versions appear identical, yet one subtly incorporates deceptive design patterns. We aimed to investigate the effectiveness of these patterns and validate the following hypotheses:
H1: Deceptive patterns are effective at influencing user decision-making.
H2: Some deceptive patterns are more effective than others.
H0: Deceptive patterns are not effective at influencing user decision-making.
The objective
This research focuses on comprehending the impact of deceptive patterns on users' decision-making within a simulated retail app. The study encompasses three primary objectives:
To Investigate Decision-Making Effect
Our foremost objective is to delve into the effects of users' decision-making behaviour while engaging with a simulated retail app.
Comparative Analysis of Deceptive Patterns
The second objective involves identifying which deceptive pattern proves most effective in influencing users' decision-making. This will be achieved by comparing the effects of various deceptive patterns with a control condition.
User Experience Investigation
The third objective is to explore the user experiences related to the use of deceptive patterns in comparison to a control condition

What are deceptive patterns
“Deceptive patterns (also known as “dark patterns”) are tricks used in websites and apps that make you do things that you didn't mean to, like buying or signing up for something”(Brignull et al., 2023)
Why deceptive patterns?
Understanding deceptive patterns is critical since it is our ethical responsibility as UX designers to provide user-centred, transparent, and trustworthy experiences. Avoiding deceptive patterns promotes trust, a positive brand image, and long-term success. Neglecting ethical design can result in legal challenges and damages to a company's reputation, ultimately causing harm to both users and the company.
Understanding deceptive patterns
Before starting the design process, I required more information about the topic at hand. My main objective was to explore the various types of deceptive patterns and assess their effectiveness in influencing user behaviour, as well as their prevalence across different digital platforms. To begin with, I conducted a secondary research study.
Web deception analysis
Mathur et al. (2019) conducted a comprehensive web deception analysis, revealing that deceptive patterns were present in 11% of 11,000 English websites.
App deception prevalence
Di Geronimo et al. (2020) explored the prevalence of deceptive patterns in mobile apps. They found that a staggering 95% of the top 240 Android apps included deceptive patterns, with the "false hierarchy" pattern being the most prevalent at 61%.
Effectiveness of deceptive patterns
In our study, we found compelling evidence that deceptive patterns are effective in influencing user behaviour. Mild deceptive patterns achieved a 25.8% sign-up rate, while severe patterns reached 41.9% (Luguri & Strahilevitz, 2021). Voigt et al. (2021) noted a 12% increase in newsletter subscriptions through the "double negative" pattern and an 11% accidental purchase rate with "sneaking." A "pre-selection nudge" led to a 33.6% acceptance rate (Utz et al., 2019). Removing the "Reject all" button in cookie banners boosted acceptance from 22% to 23% (Nouwens et al., 2020). These findings emphasise the diverse effects of deceptive patterns on user behaviour.
Design exploration
Identifying deceptive patterns
We took a careful look at various apps and websites, including deceptive.design, to learn about different deceptive patterns in use. We also studied articles and posts that provided real-world examples of deceptive patterns across digital platforms. This research allowed us to create a blueprint for designing the app with these deceptive patterns.

Ideation
Visual concepts for screen variations
During the ideation phase, we aimed to keep the user journey as straightforward as possible, adhering to the primary interaction path typical of a shopping platform. In both conditions, we maintained the core user path, with minor alterations to buttons, text, and page layout to introduce deceptive patterns. During this process, it also allowed us to spur creative thinking on enhancing user navigation, reducing friction, and ensuring a smoother journey.

Visual concepts: Screens with deceptive patterns
Sketching out the visual concepts for the app served as a valuable tool for visualising how various ideas might converge. In this ideation phase, we're still exploring and refining our choices regarding which deceptive patterns to incorporate into the design. We're also considering the most effective placement of each deceptive pattern within the screens and interactions. This process was instrumental in forming a unified vision for my final design concepts.

Design prototyping
Designing an experience, and putting it to the test
With the help of two of my supervisors, we were able to discuss, test and iterate the design until we felt confident in our product decisions.
We then produced a multitude of prototypes, which, in turn, assisted in the careful selection of deceptive patterns to be incorporated into the experiment while continuously improving the overall design of the app.

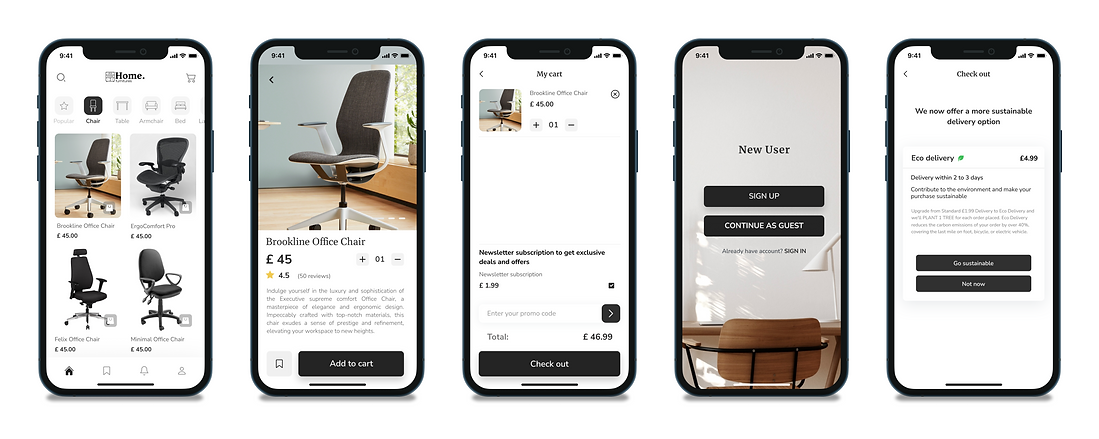
Final design
Bringing Home Furniture to life
Transitioning to the design of high-quality screens in Figma, my aim was to make the interface visually and functionally identical, except for small changes in buttons, text, and page layout to introduce deceptive patterns. All the while, ensuring that the designs remained user-friendly and intuitive.
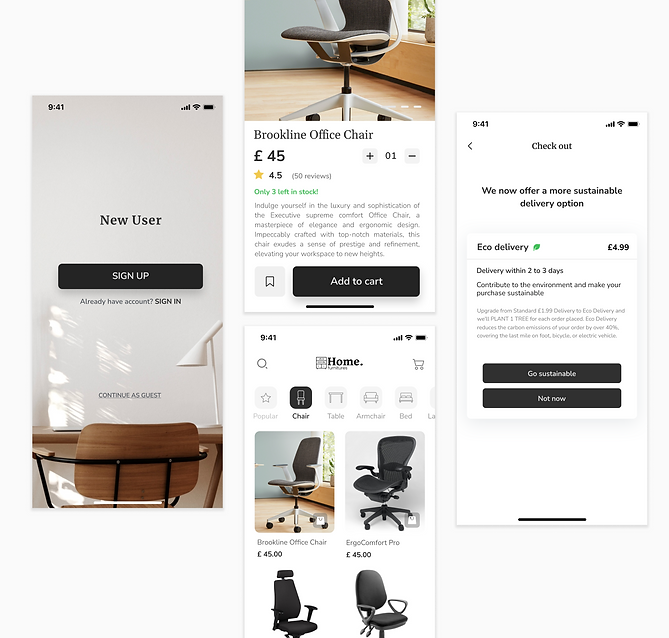
Challenge 1
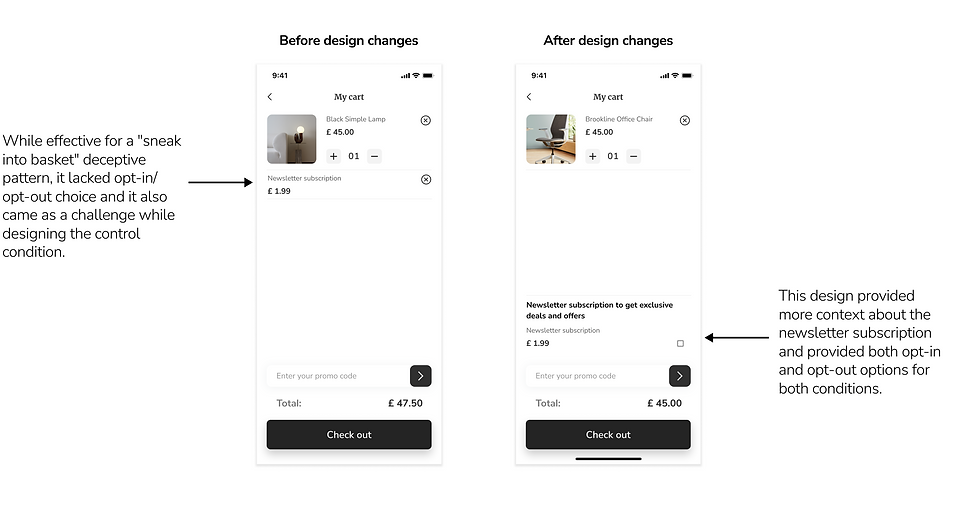
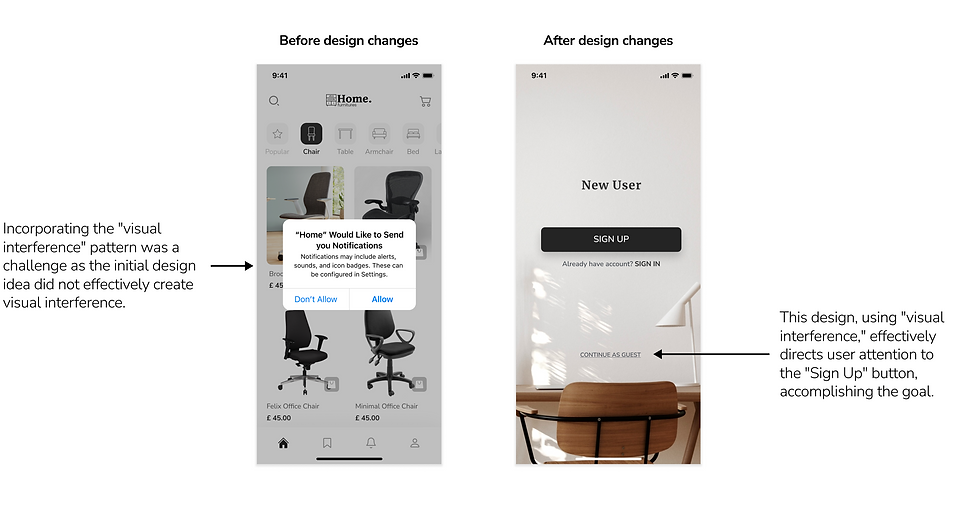
Crafting clean and deceptive designs
In our pursuit of comprehending the effects of deceptive patterns, we faced the challenge of creating two versions of the app: one with deceptive patterns and another entirely clear of any deceptive elements. The catch was to maintain an identical UI design in both versions. Achieving this involved exploring different approaches to seamlessly interchange designs, allowing us to study their distinct impacts on user behaviour.

Control condition
Challenge 2
Measuring user interactions
Our second challenge revolved around ensuring that the UI elements in both versions of the app were quantifiable. We needed to collect data on user interactions, including clicks and the options users selected. The collected data will be analysed comprehensively, shedding light on the influence of deceptive patterns and their effects on user choices and behaviour during the study.
Deceptive pattern condition
A/B testing
We conducted A/B testing using Quant-UX, with 51 participants. Out of these, 25 participants were assigned to the control condition, while 26 participants were assigned to the deceptive pattern condition. It is noteworthy that in the deceptive pattern condition, more than 80% of the participants were misled into performing tasks that they had not originally intended to do. Moreover, the user experience in the deceptive pattern condition was noticeably poor. These findings clearly indicate that deceptive patterns have a significant impact on user decision-making.
Takeaways
As previously mentioned, digital platforms have been known to use deceptive patterns to manipulate users into performing tasks they did not intend to. Our project is just a small part of a larger effort to understand how these patterns work and how they influence user behaviour. One key takeaway from this project was realizing how even small changes in font, text, colour, or layout can have a significant impact on how information is presented, highlighting the powerful effects of design.
References
-
Di Geronimo, L., Braz, L., Fregnan, E., Palomba, F., & Bacchelli, A. (2020). UI Dark Patterns and Where to Find Them: A Study on Mobile Applications and User Perception. Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1145/3313831.3376600
-
Luguri, J., & Strahilevitz, L. J. (2021). Shining a Light on Dark Patterns. Journal of Legal Analysis, 13(1), 43–109. https://doi.org/10.1093/jla/laaa006
-
Mathur, A., Acar, G., Friedman, M. J., Lucherini, E., Mayer, J., Chetty, M., & Narayanan, A. (2019). Dark Patterns at Scale: Findings from a Crawl of 11K Shopping Websites. Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, 3(CSCW), 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1145/3359183
-
Nouwens, M., Liccardi, I., Veale, M., Karger, D., & Kagal, L. (2020). Dark Patterns after the GDPR: Scraping Consent Pop-ups and Demonstrating their Influence. Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1145/3313831.3376321
-
Utz, C., Degeling, M., Fahl, S., Schaub, F., & Holz, T. (2019). (Un)informed Consent: Studying GDPR Consent Notices in the Field. Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, 973–990. https://doi.org/10.1145/3319535.3354212
-
Voigt, C., Schlögl, S., & Groth, A. (2021). Dark Patterns in Online Shopping: Of Sneaky Tricks, Perceived Annoyance and Respective Brand Trust. In F. F.-H. Nah & K. Siau (Eds.), HCI in Business, Government and Organizations (pp. 143–155). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77750-0_10
Reach out to me!
Interested in working together?
Let's Connect!
©️ 2023 Lipoksanen Jamir


